A VPN is an essential tool for anyone who cares about digital privacy. It’s an easy-to-use way to protect yourself while browsing on public Wi-Fi.
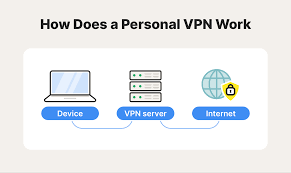
Without a VPN, everything you do on the internet is visible to your ISP. This includes the websites you visit, the apps you use, and your browsing history. With a VPN, all of that data is encrypted and hidden from your ISP.
Authentication
A VPN uses authentication to verify that a device is allowed to access network resources. The primary form of authentication is a username and password combination, but many VPNs use more than one factor to authenticate users.
Role-based access control is another important method to help secure VPNs. It assigns user roles within a business and allows them to access only those services and files that are necessary for their role. This minimizes the impact of a compromised account by limiting what a hacker can do.
Companies with offices in multiple fixed locations can use a site-to-site VPN to connect those locations into a single network, making it easier for remote workers to work from home or on the go. A VPN can also be used to circumvent censorship by connecting to servers in countries with a freer Internet. For example, journalists in repressive countries use VPNs to keep their sources and work private. Online shoppers can use VPNs to avoid price discrimination based on their location or perceived ability to pay.
Encryption
When a VPN is on, data that goes to and from your device gets encrypted before it hits the Internet. This prevents anyone from seeing what you’re doing online, even if they have access to your network.
In the past, VPNs were used to help remote workers connect to their corporate networks. But as privacy concerns grew, people started using them at home as well.
Now, almost everyone who uses the Internet regularly benefits from using a VPN. Journalists who need to protect their sources use them, businesspeople with sensitive work in different locations need them for cybersecurity, and people living in undemocratic or illiberal states use them to get around government censorship.
When choosing a VPN, consider the provider’s data usage policies and logging policy. Also, make sure to look for a VPN that offers simultaneous connections, because you may want to use it on multiple devices at once. Some free VPNs may limit how much data you can use during a period of time, while paid versions typically do not.
Routing
A routing protocol enables you to choose the best path for data transmission across a network. It also helps optimize the performance of real-time applications like videoconferencing and online gaming. Quality of service (QoS) is a type of routing that ensures that traffic for important applications gets priority over less time-critical data.
The routers that connect the Internet use a variety of routing protocols. One popular type of routing is BGP, which lets different autonomous systems share information about routes to other networks. BGP also supports dynamic routing, which allows each router to automatically update its routing table when it discovers a new route that is better than the previous one.
VPNs use a variety of technologies to create secure, private connections between office locations. These technologies allow businesses to expand their private internal network without the high cost of leased lines. They also enable employees to work from home or the office and use technology like desktop sharing to collaborate on projects. To get more information, head on to v2ray 机场怎么选 to know more.
Speed
The primary reason for slow VPN connections is the time required to encrypt and decrypt data, as well as the round-trip time from the VPN server to your device. Some VPN services also prioritize bandwidth for users who need it most, which can result in slower connections.
In addition, the type of VPN protocol you use can have a significant impact on performance. For example, PPTP has more speed limitations than OpenVPN. Finally, if you use a free VPN service, your connection may be slowed by malware or other problems that can drain your bandwidth and affect performance.
To speed up your VPN, try closing any unused tabs or applications on your computer that could be using up resources and affecting your internet or VPN connection. You should also restart your router and any other connected devices. Restarting these devices gives them a fresh start and can sometimes solve VPN speed issues.
